
It shows where a value starts, ends and how it gets there incrementally.

Waterfall charts effectively display the cumulative effect of sequential positive and negative values.
ADVANCED WATERFALL CHART TABLEAU HOW TO
The above method explains how to create a Waterfall Chart in Tableau, which some also refer to as a ‘Flying Chart’ or ‘Bridge Chart.’ Waterfall Charts offer an effective way to analyze the upswings and downturns of a business.Tableau - Waterfall Charts Previous Page Next Page These charts have varying applicability in several streams, like population control, birth rate, death rate, business profit and loss, supermarkets, etc. Helps to get net, cumulative, profit, and loss valuesĦ. Possesses data visualization techniquesĥ. Provides improved insights into business dataĤ. Functions as a means of communication within the teamģ. A medium of information within the concerned party.Ģ. Importance of Waterfall Chart in Tableauġ. No two charts can be similar, and chart customization varies from person to person. These are the basics of the Waterfall chart. Refer to the below image for data marking: The chart itself explains why it is termed Waterfall (as the data represent one single value − +ve/=ve). When one hovers the cursor over the Gantt bars, one can see the ‘Positive/Negative’ values associated with each of them. The data visualized above is a Gantt chart view. Note: Drag and drop this newly created ‘Negative Value’ to the ‘Size’ section (present in Marks).ġ5. This newly created ‘Negative value’ will be present in the ‘DATA’ section. Now one must pull the ‘Negative Value’ parameter (the one just created refer to the above image) in the ‘SIZE’ (present in the MARKS section). After one selects the ‘Calculated Fields,’ there will be a dialogue box to rename them (generally choose a relevant name like “Negative Profit”). Note: We can see the ‘DATA’ and ‘ANALYTICS’ sections in the red box.ġ3. Now proceed to select the ‘CREATE CALCULATED FIELD.’ Refer to the below image: To do this, one makes a simple adjustment: create a calculated measure by right-clicking anywhere on the ‘DATA’ field. The bars (or the data) on top of this Gantt chart are required.
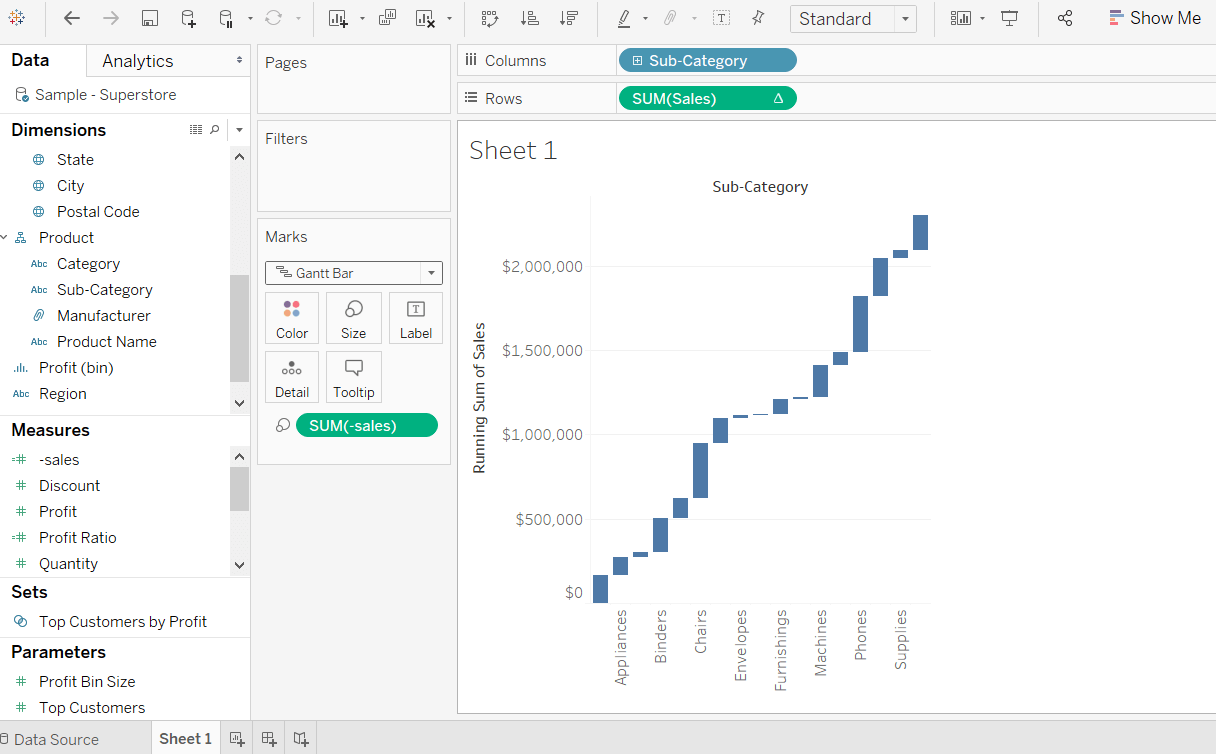
Now one can view the data’s Gantt chart however, it requires several corrections.ġ2. Click on the ‘Marks’ drop-down menu and select the ‘Gantt’ chart. It contains all the data enhancement techniques.ġ0. To achieve this, we will navigate to the ‘MARKS’ section (on the left-hand side) of the dashboard. Next step is to convert the chart into Waterfall Chart in Tableau. The above image shows the ‘Running Total’ for the selected list of items.ĩ.
After making changes to the graph, it will result in something as below:Ĩ. Hence, SUM > QUICK TABLE CALCULATION > RUNNING TOTALħ. As one right-clicks on the ‘SUM’ present in the ‘Rows’ section, one will get ‘Quick Table Calculation’ and ‘Running Total.’ Make certain changes in the graph to display the ‘Running Total’ details. Its form must be manipulated from here on.Ħ. Now the basic layout of the graph is ready however, this is not a Waterfall Chart in Tableau but a bar chart. The subcategory is a measuring dimension, i.e., a list of items.ĥ. Drag and drop the sub-category (or the items’ name) in the ‘Column’ section of the dashboard (please see the below image). Once done, one can see the bar chart for ‘Profit’ (blue bar).Ĥ. Once the data set is fed into the Tableau application, select the ‘SUM’ category and drag and drop in the ‘Rows’ section as mentioned below:ģ. Thus, we will be measuring profit in relation to the given items.Ģ.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
